As an advanced processing technology, precision laser cutting boasts advantages such as high flexibility, stress-free non-contact processing and a high level of intellectualization. Featuring narrow kerfs, low material loss and no need for molds, it is applicable to the processing of almost all materials. It has become a core solution for precision manufacturing in various industries and plays an irreplaceable role in numerous high-end fields:
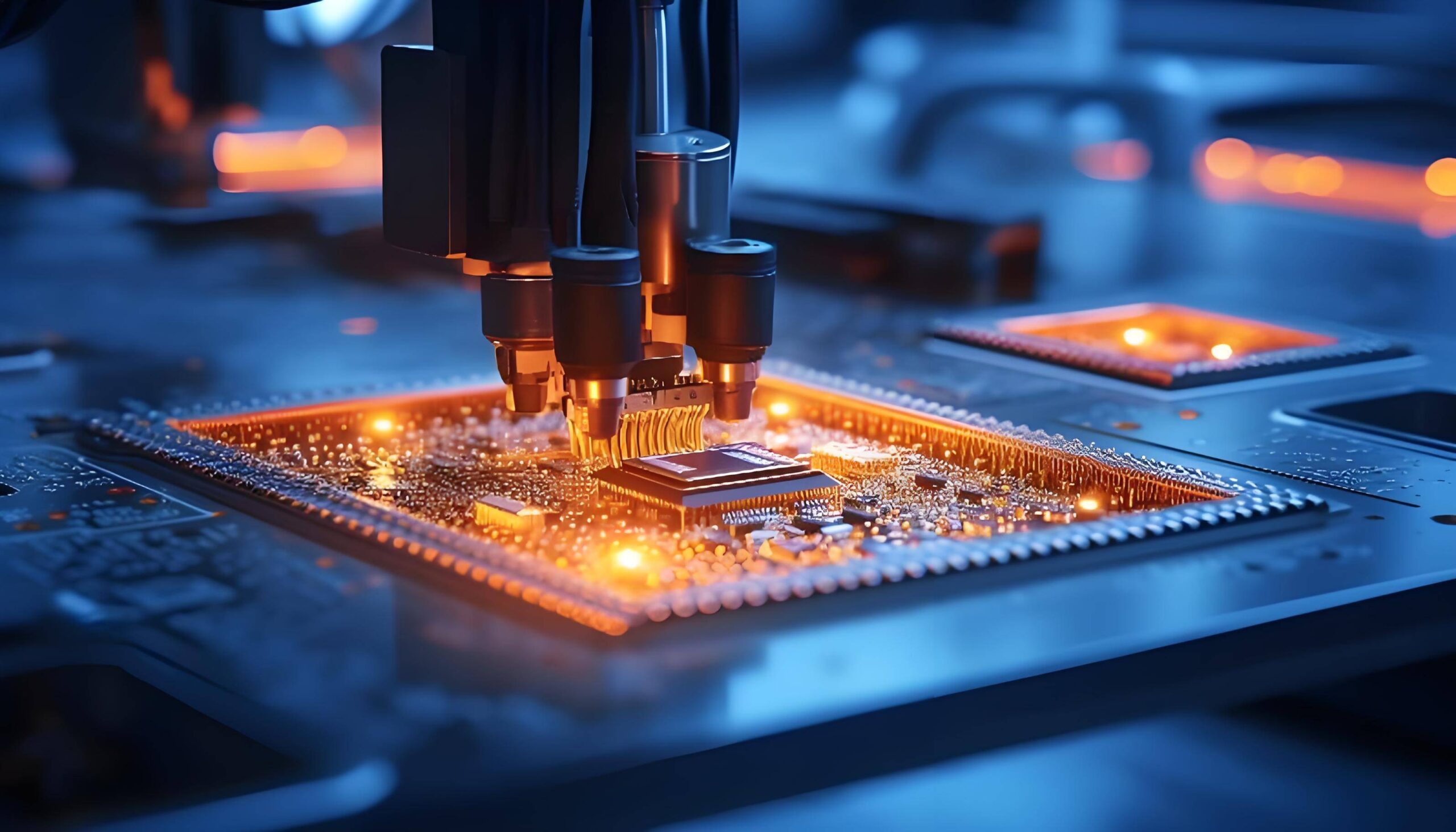
1. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
All types of components in the electronics and semiconductor industry are trending towards "light weight, thinness, shortness and miniaturization", with highly integrated internal structures, imposing extremely high requirements on the precision, appearance and consistency of parts.
The non-contact processing of laser cutting avoids damage to fragile circuits caused by mechanical stress, making it ideal for processing a large number of components and integrated circuits widely used in products such as PCBs, mobile phones and tablet computers.

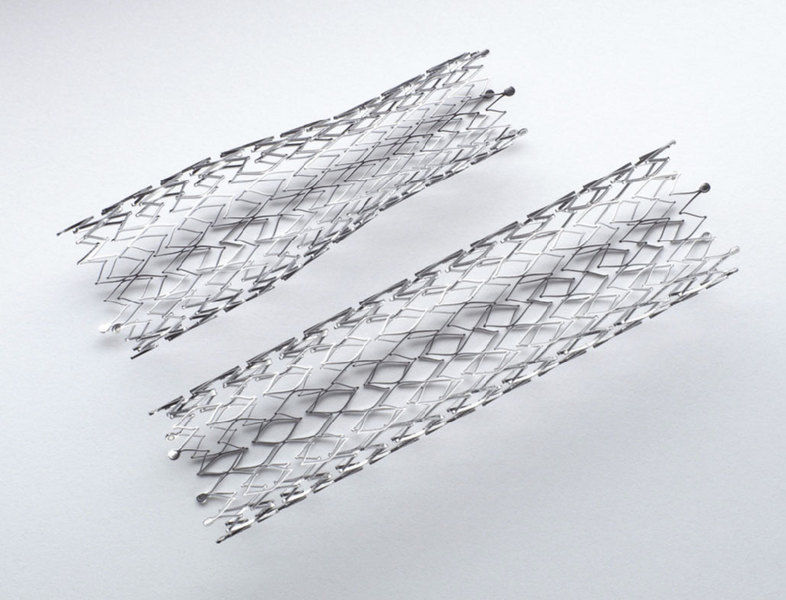
2. Medical Device Industry
Medical devices have extremely stringent requirements for safety, biocompatibility and precision. Laser cutting enables aseptic and pollution-free processing and can handle special materials required for implants. The most typical case is cardiac stents, where lasers are used to cut extremely complex mesh structures on tiny nitinol or stainless steel tubes.
In addition, it is also applied to the processing of precision components such as endoscope parts and interventional catheters.
3. New Energy Vehicles
The new energy vehicle industry is currently in a stage of rapid development, with a large number of emerging technologies applied in it.
Precision laser cutting is widely used in the processing of precision components in automotive batteries and motors, such as the cutting of explosion-proof valves for battery packs, tab cutting for battery cells, cutting of aluminum/copper bars for battery modules, as well as the cutting of silicon steel sheets for stators and rotors in motors.
It is also used for engine fuel injectors, sensor housings, gears, transmission system parts and other components.
4. Aerospace Industry
Aerospace components are usually made of expensive special alloys and composite materials, which have high hardness and are difficult to process.
The non-contact and high-precision characteristics of laser cutting can maximize the stability of cutting quality and ensure part strength. Typical applications include the cutting of cooling film holes on engine turbine blades and combustion chamber components, as well as the precise trimming and hole drilling of carbon fiber composite fuselage panels and wing components.

5. Luxury Industries such as Watches and Jewelry
Due to the high price of their products, these industries have high requirements for design complexity and personalization, and the materials used are precious.
Laser cutting can perfectly create complex and delicate patterns with extremely low material loss. For example, it is applied to the precision processing of tiny components in mechanical watches such as gears, escape wheels, dials and watch cases, the cutting of hollow patterns on rings and pendants, and the pre-welding cutting of precious metal chain links.

Compared with traditional mechanical cutting, the various advantages of precision laser cutting have made it a universal solution to the precision manufacturing challenges in various industries.